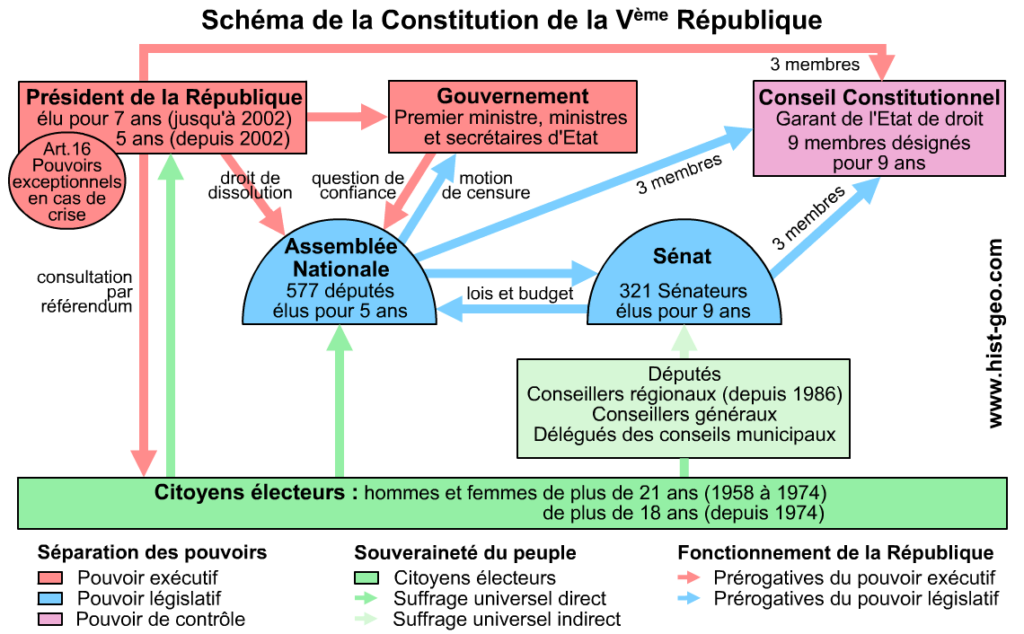
It is a presidential regime in which the Constitution will strengthen the powers of the President of the Republic by a referendum of 28 October 1962 which consecrates the election of the President of the Republic by direct universal suffrage.
He appoints the Government, headed by the Prime Minister, who is the result of the majority in the legislative elections. He can consult the people by referendum and govern by ordinance only in case of serious situation.
He also enjoys, by Article 16, full powers in the event of an exceptional situation.
Thanks to article 38, the President of the Republic may also request the authorization of Parliament to take by ordinance, for a limited period, measures that are normally within the domain of the law.
Article 49.3 also allows the Government to pass laws without a vote in Parliament.
Parliament, composed of the National Assembly and the Senate, votes laws and controls the Government. Deputies to the National Assembly are elected every five years in legislative elections.
Justice is exercised by magistrates. It punishes violations of the law, imprisonment or other penalties provided for by law. It settles disputes between individuals or companies, and between citizens and the administration.
Parliament therefore has reduced legislative power in order to avoid a return to the assembly system. Chambers control measures are introduced.
The main features of this Constitution are:
- Presidential system and the introduction of direct universal suffrage: all citizens can give their political opinion in order to directly elect the President of the Republic. This direct election also allows the power in place to be more legitimate. The parliamentary system did not involve the election of the president by universal suffrage, unlike the presidential system.
- Bipolarization: the Constitution must make it possible to avoid partitocracy. The use of universal suffrage allows all parties to express themselves to “contribute to the expression of suffrage”, but the two-round majority system leads to a two-party system, and a composition of governments according to these results, which removes any conciliation from governments with many small parties.
- Revision of the Constitution: The Constitution may be revised (Article 89 of the Constitution). It has been revised about fifteen times until today.
